Current image and head up display
The current image panel (SKG standard GUI), is divided in 5 zones:
1. Check boxes and slider that allow to show/hide and control the transparency of the head up display (HUD). The negative check box allows to inverse the current image (background in white, and bright objects and stars black)
2. The current image output by the guiding camera
3. The level bar with the low/high stretch sliders and a button that resets the sliders to their maximum values
4. The information about the current image (ADU, X and Y position of the mouse pointer, X and Y RMS values)
5. Zoom command buttons
To control the transparency of the head up display, just left click, hold the left button down and move to the left to make it more transparent and to the right to make it less transparent.
To display the ADU value of a selected pixel in the image, just left click the image on the selected pixel.
To zoom in/out just use the mouse wheel or use the Fill, 2x, 5x or 10x command buttons.
To pan the zoom image, just left click, hold the left button down and move the mouse to the direction you want to pan.
To fit the image inside the view port, click the Fit button.
To restore the previous zoom, click the Undo button.
To restore the next zoom, click the Redo button.
To stretch the image, just click on the left button to the low/high slider, hold the left button down and move it to the desired level
To restore the stretch to the maximum levels, just click the "Max" button
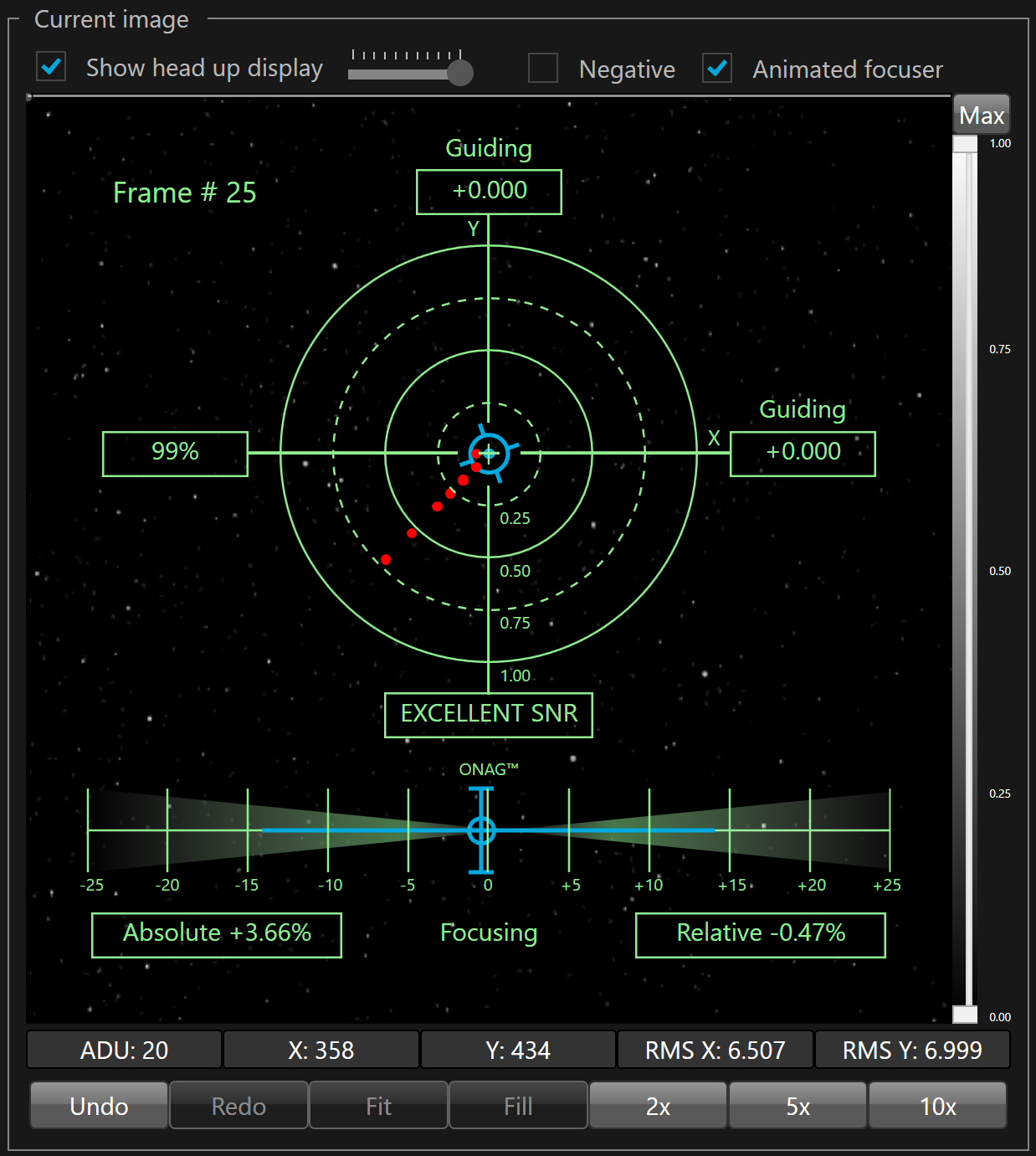
The HUD displays the following information:
- In the upper left corner, a label shows the number of the last guider frame displayed in the view port
- In the left box of the horizontal axis, the ADIC correlation level of the current frame vs the reference frame (between 0% and 100%)
- In the bottom box of the vertical axis (Y), the Signal-To-Noise evaluation (None, Poor, Fair, Good, Excellent)
- In the top box of the vertical axis, the error on the Y axis of the guider camera. Above the error, the label display "Guiding" when SKG is sending corrections to the guider relay and "Idle" when the correction has been disabled for this axis, including the min and max moves.
- In the right box of the horizontal axis, the error on the X axis of the guider camera. Above the error, the label display "Guiding" when SKG is sending correction to the guider relay and "Idle" when the correction has been disabled for this axis,, including the min and max moves.
- When dithering is enabled or in progress a label shows the its status in the upper right corner.
- Below the Signal-To-Noise evaluation, the auto-focus is displayed as two scales starting from the center at 0. These scales represents the relative roundness of the astigmatism caused by the ONAG when the IR light is crossing the beam splitter.
- The blue circle crossed by a vertical line and two horizontal lines on both extremities represent the current relative roundness.
- The blue horizontal line centered in the scales represent the size of the critical focus zone. When the current relative roundness is inside the blue line that means the instrument is within its critical focus zone. When it is outside the blue line the instrument is intra or extra focal.
 The length of the blue line can only be calculated after a successful regular focuser calibration. If the calibrated system gain is empty the blue line does not appear.
The length of the blue line can only be calculated after a successful regular focuser calibration. If the calibrated system gain is empty the blue line does not appear.
 In the lower left box, a label shows the absolute roundness in percent
In the lower left box, a label shows the absolute roundness in percent In the lower right box, a label shows the relative roundness in percent.
In the lower right box, a label shows the relative roundness in percent.
 If average roundness checkbox is checked in the focusing settings, the average values are used. Otherwise the roundness of the last frame is used.
If average roundness checkbox is checked in the focusing settings, the average values are used. Otherwise the roundness of the last frame is used.
 In the lower middle, a label shows "Focusing" when SKG is sending corrections to the focuser relay and "Idle" when the correction has been disabled, including stop gap.
In the lower middle, a label shows "Focusing" when SKG is sending corrections to the focuser relay and "Idle" when the correction has been disabled, including stop gap.
The current X and Y errors are displayed by a rotating blue circle with spikes. When the X and Y errors are close to zero, this blue circle is centered with the bull's-eye, while it moves away from from it, according the amount of error measured by SKG, otherwise.
The tracking window limit is materialized by 4 circles, the outer circle represent 100% of the tracking window size, the inner circle represent 25% of the tracking window, the second circle from the center represent 50% and the third circle from the center represent 75%.
 The history of the guiding errors are materialized by dots. This is a scatter plot with blue and red dots. The blue dot shows errors that are below the pixel guider FOV, including binning, while the red dots shows the errors that are above the guider pixel FOV.
The history of the guiding errors are materialized by dots. This is a scatter plot with blue and red dots. The blue dot shows errors that are below the pixel guider FOV, including binning, while the red dots shows the errors that are above the guider pixel FOV.